
Theoretical principles of fluid management according to the physicochemical Stewart approach | Semantic Scholar
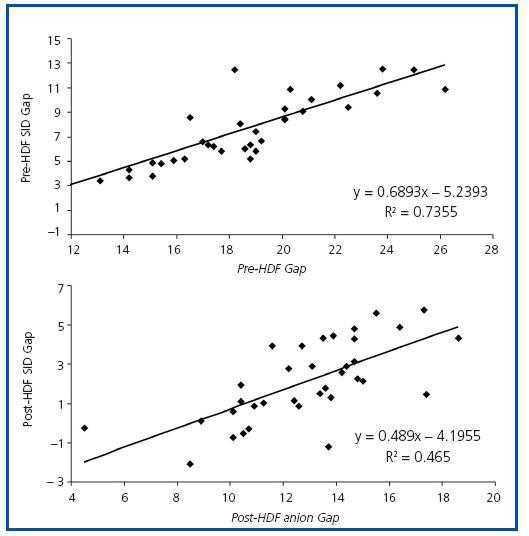
Does methodology of Stewart-Fencl improve characterization of acid-base status in patients on hemodiafiltration? | Nefrología

Utility of Stewart's Approach to Diagnose Missed Complex Acid–Base Disorders as Compared to Bicarbonate-anion Gap-based Methodology in Critically Ill Patients: An Observational Study

Stewart's approach: Just a heresy or another lens into acid‐base physiology? - Vasileiadis - 2021 - Acta Physiologica - Wiley Online Library

An Easy Method of Mentally Estimating the Metabolic Component of Acid/base Balance Using the Fencl-Stewart Approach | Semantic Scholar

Strong ions, weak acids and base excess: a simplified Fencl–Stewart approach to clinical acid–base disorders - ScienceDirect
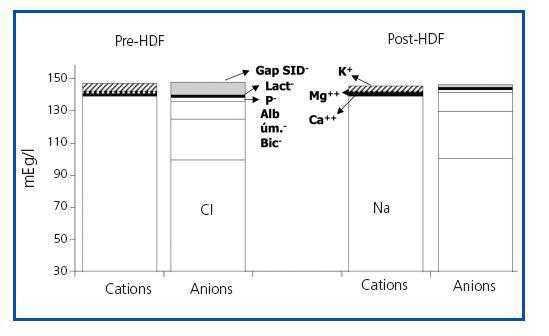
Does methodology of Stewart-Fencl improve characterization of acid-base status in patients on hemodiafiltration? | Nefrología
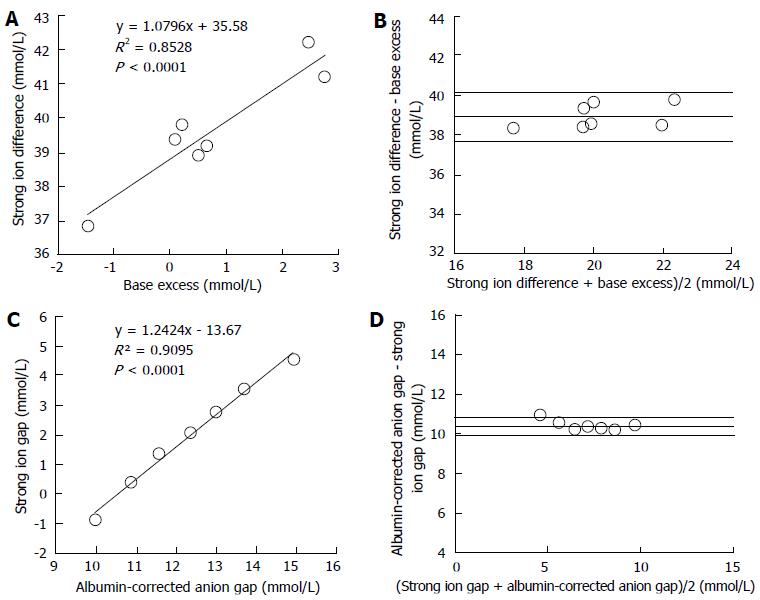
Has Stewart approach improved our ability to diagnose acid-base disorders in critically ill patients?

PDF) Strong ions, weak acids and base excess: A simplified Fencl-Stewart approach to clinical acid-base disorders

Strong ions, weak acids and base excess: a simplified Fencl–Stewart approach to clinical acid–base disorders† - British Journal of Anaesthesia

An Easy Method of Mentally Estimating the Metabolic Component of Acid/base Balance Using the Fencl-Stewart Approach | Semantic Scholar

An Easy Method of Mentally Estimating the Metabolic Component of Acid/base Balance Using the Fencl-Stewart Approach | Semantic Scholar
![PDF] Strong ions, weak acids and base excess: a simplified Fencl-Stewart approach to clinical acid-base disorders. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Strong ions, weak acids and base excess: a simplified Fencl-Stewart approach to clinical acid-base disorders. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/c80b512c7849b9416e074efe4e3524cbc499a82d/3-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Strong ions, weak acids and base excess: a simplified Fencl-Stewart approach to clinical acid-base disorders. | Semantic Scholar

Diagnosing metabolic acidosis in the critically ill: bridging the anion gap, Stewart, and base excess methods | Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d'anesthésie

Strong ion gap (SIG) is the difference SID a and SID e. The SIG is an... | Download Scientific Diagram

Clinical review: Acid-base abnormalities in the intensive care unit -- part II. - Abstract - Europe PMC
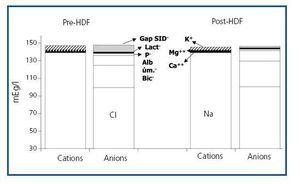
Does methodology of Stewart-Fencl improve characterization of acid-base status in patients on hemodiafiltration? | Nefrología

Acid–base status of critically ill patients with acute renal failure: analysis based on Stewart–Figge methodology | Critical Care | Full Text







